Comprehensive Guide to Orthopedic Surgery Tools
Orthopedic surgery tools play a critical role in modern medicine, enabling surgeons to perform complex procedures with precision and efficiency. As the demand for orthopedic surgeries continues to rise, understanding these tools' types, uses, and innovations becomes essential for both healthcare professionals and patients alike. In this guide, we will delve into the various categories of orthopedic instruments, their specific applications, and recent advancements that are shaping the future of orthopedic surgery.
Understanding Orthopedic Surgery
Orthopedic surgery involves diagnosing, treating, and rehabilitating conditions related to the musculoskeletal system. This includes bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, and muscles. The precision offered by orthopedic surgery tools is crucial in addressing a wide array of issues, from broken bones to degenerative diseases such as arthritis.
Key Categories of Orthopedic Surgery Tools
Orthopedic instruments can be broadly categorized into the following types:
- Diagnostic Tools: Instruments used for examination and diagnosis.
- Surgical Instruments: Tools specifically designed for invasive procedures.
- Rehabilitation Tools: Instruments aiding in patient recovery post-surgery.
Diagnostic Tools in Orthopedics
Before any surgical intervention, accurate diagnosis is paramount. Various orthopedic surgery tools are designed to facilitate this process:
- Radiography Equipment: X-rays are the most common diagnostic tool, providing a clear image of bones and joints.
- MRI Machines: Magnetic Resonance Imaging is crucial for visualizing soft tissues, such as ligaments and cartilage.
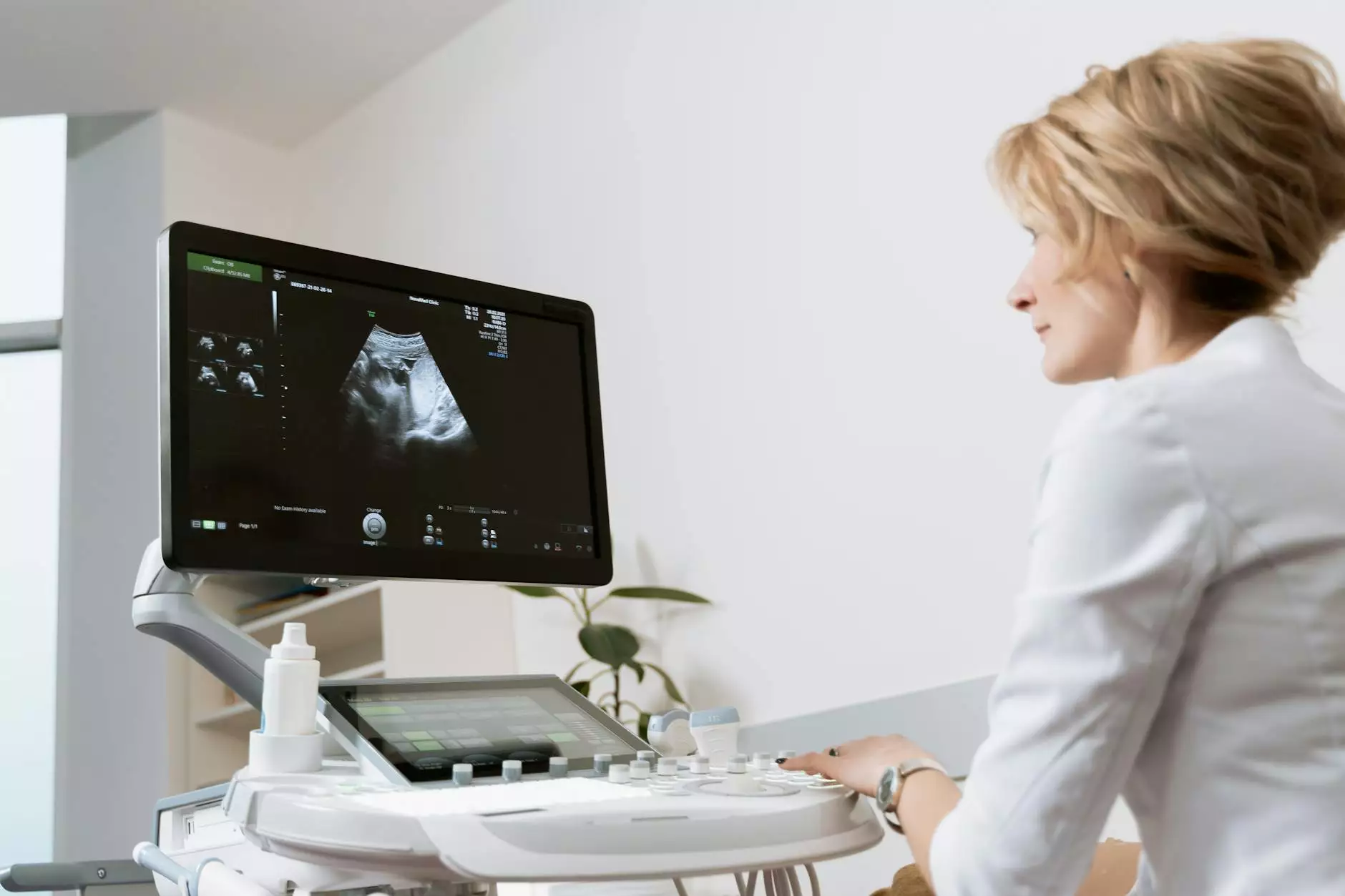
- Ultrasound Devices: These instruments help in assessing soft tissue injuries and are advantageous due to their non-invasive nature.
Surgical Instruments Used in Orthopedic Procedures
The success of orthopedic surgeries significantly relies on the efficacy of surgical instruments. Here are some essential orthopedic surgery tools used in various procedures:
1. Scalpels and Blades
Scalpels are fundamental to surgery, offering precision cuts through tissue. Different blade shapes serve diverse purposes, from making incisions to excising tissue.
2. Scissors
Orthopedic scissors, often designed with sharp cutting edges and pointed tips, allow surgeons to cut through tough tissue types, including fascia and muscle.
3. Forceps
Forceps are indispensable tools in various surgical scenarios, providing the ability to grab, hold, or manipulate tissues and organs during intricate procedures.
4. Drills and Saw Blades
In orthopedic surgeries, such as joint replacements, specialized drills and saw blades are used to ensure accurate cuts and bone shaping. Innovations in this category, such as battery-operated and laser-guided drills, enhance precision and safety.
5. Plates and Screws
Internal fixation often employs plates and screws to provide stability to fractured bones. Understanding the different materials and designs, such as titanium and biodegradable options, can aid in selecting the appropriate fixation strategy.
Tools for Minimally Invasive Surgery
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) has transformed orthopedic techniques. This approach minimizes tissue damage, reduces recovery time, and improves patient outcomes. Tools associated with MIS include:
- Endoscopes: These flexible tubes equipped with cameras allow surgeons to see inside the joint without large incisions.
- arthroscopes: A type of endoscope specifically designed for joint surgeries.
- Tubular Retractors: Used to widen small incisions while minimizing tissue disruption.
Rehabilitation Tools Post-Surgery
After surgery, the journey to recovery involves various rehabilitation tools aimed at restoring function:
- Braces and Orthoses: Supportive devices help in stabilizing injured areas and assist in recovery.
- Physical Therapy Equipment: Tools such as resistance bands, weights, and balance boards are essential for rehabilitation exercises.
- Hot and Cold Packs: Used for pain management and reducing swelling, these basic therapeutic tools are invaluable in postoperative care.
Innovation and Advancements in Orthopedic Tools
As technology advances, the field of orthopedics is experiencing significant innovations that enhance the functionality and efficiency of surgical tools:
Robotics in Orthopedic Surgery
Robotic-assisted surgery has emerged as a game-changer, allowing for high precision and control. Robots like the Mako Surgical System have gained popularity, especially in knee and hip replacement surgeries, improving outcomes through enhanced accuracy.
3D Printing in Orthopedic Tools
3D printing technology has transformed the production of surgical instruments and implants, allowing for personalized tools and customizable implants that conform to individual patient anatomy, thus improving compatibility and healing.
Smart Surgery Tools
Integrating technology, such as sensors and AI, into orthopedic surgery tools aids in providing real-time feedback. This innovation enhances the effectiveness of surgeries, reduces errors, and assures better patient outcomes.
Conclusion: The Future of Orthopedic Surgery Tools
As we continue to push the boundaries of medical science, the role of orthopedic surgery tools becomes increasingly pivotal. Their evolution, driven by technology and innovation, promises to enhance surgical precision, improve patient care, and reduce recovery times. For healthcare providers looking to stay at the forefront of orthopedic surgery, choosing quality tools is paramount; this not only impacts the surgical outcomes but the overall health and well-being of their patients as well. Organizations such as new-medinstruments.com are at the forefront of providing high-quality orthopedic tools, meeting the evolving demands of the healthcare sector.
By investing in advanced orthopedic tools and staying informed about new technological advancements, surgeons can significantly enhance their practice. As the field evolves, patients can expect better surgical experiences and improved recovery outcomes.